
Revolutionizing Enterprise Coding: The 25% AI Milestone of 2025
December 19, 2025 / Bryan ReynoldsExecutive Summary
The landscape of enterprise software development underwent a seismic shift in November 2025. In a disclosure that effectively ends the debate on the utility of generative AI in production environments, Google and Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai announced that artificial intelligence now generates over 25% of the company's new code. This revelation, paired with the launch of the reasoning-capable Gemini 3 model and a historic surge in Alphabet's market capitalization to nearly $4 trillion, signals that the industry has moved from the "preparation phase" to "full implementation."
This report provides an exhaustive analysis of this inflection point for the B2B executive. We explore the mechanics and implications of "Vibe Coding," the technical superiority of the new Gemini 3 architecture, and the critical security vulnerabilities—specifically in Java and enterprise stacks—that accompany this velocity. Drawing on data from Veracode, Gartner, and McKinsey, we outline a governance framework for the C-suite to harness AI's speed without succumbing to the crushing weight of "contextual technical debt."
1. The Inflection Point: From Experimentation to Full Implementation
For the past three years, the B2B technology sector has existed in a state of tentative exploration regarding generative AI. Pilot programs, sandboxes, and "innovation labs" were the norm. However, late 2025 marked the definitive end of this experimental era.
1.1 The "25% Code" Milestone
On November 26, 2025, during a pivotal conversation with Logan Kilpatrick of Google's AI Studio team, Sundar Pichai quantified the impact of AI on Google's own internal operations. He revealed that more than 25% of all new code generated at Google is now written by AI.
This statistic is not merely a measure of volume; it is a testament to reliability. Google operates one of the largest and most complex monolithic codebases in the world. For the company to entrust a quarter of its incoming code stream to artificial intelligence suggests a level of maturity in tooling and governance that far exceeds simple "auto-complete" functionality. Pichai emphasized that while AI generates the code, it is "reviewed and accepted by engineers," maintaining a crucial layer of human oversight.
This transition signifies that Google has successfully moved past the "preparation phase" and entered "full implementation mode".
For the B2B executive, this serves as a critical benchmark. If the creators of the technology are leveraging it for a quarter of their foundational output, the operational risk of not adopting AI-augmented development has now eclipsed the risk of adoption.
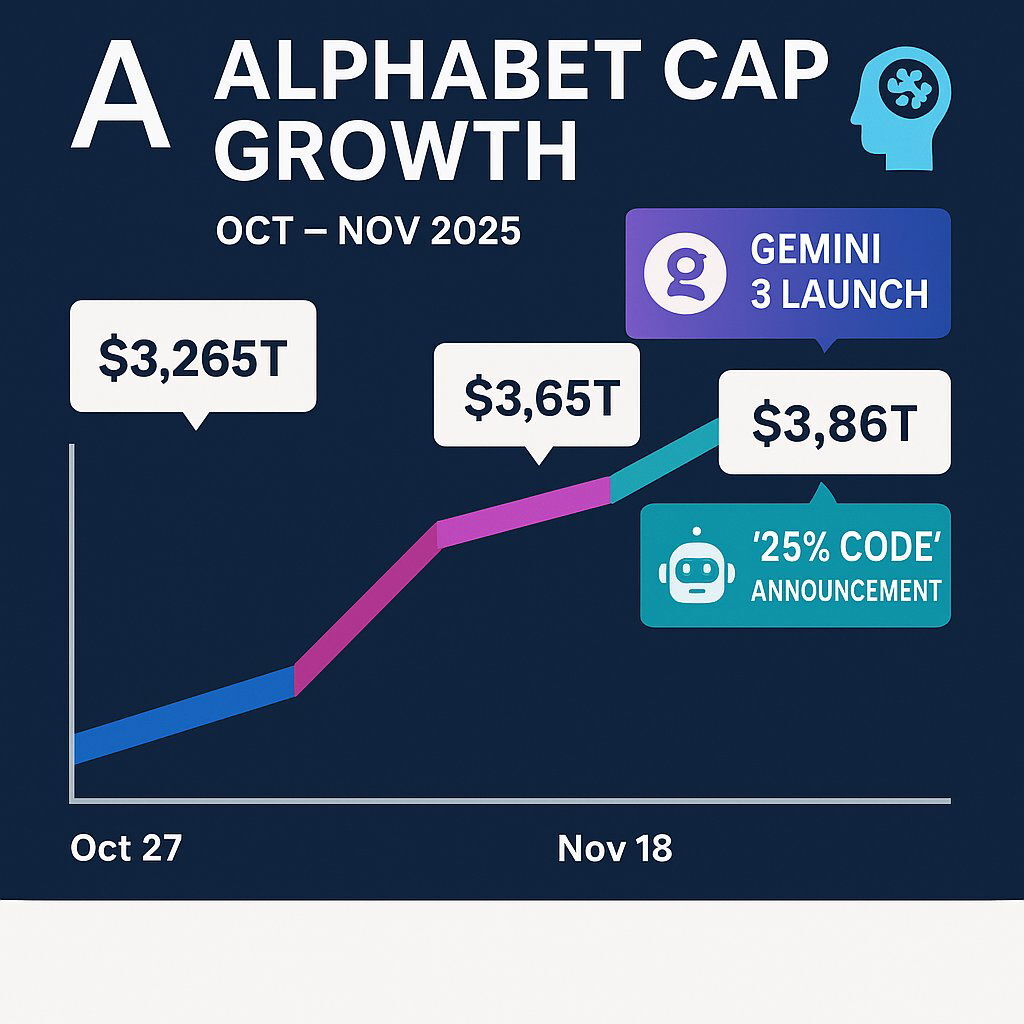
1.2 The $3.86 Trillion Market Validation
The financial markets have responded to this operational shift with overwhelming optimism. Coinciding with Pichai's interviews and the release of Gemini 3, Alphabet's stock rallied nearly 70% throughout the year, culminating in a market capitalization of approximately $3.86 trillion by late November 2025.
This valuation positions Alphabet as the world's third most valuable company, trailing only Nvidia and Apple, and places it within striking distance of the $4 trillion milestone. The surge is driven by a convergence of factors:
- Operational Efficiency: The "25% code" metric implies a significant decoupling of revenue growth from headcount growth, promising higher operating margins.
- Hardware Independence: Reports of multibillion-dollar negotiations to rent Google's Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) to Meta suggest that Google is successfully diversifying beyond advertising into high-performance AI hardware, directly challenging Nvidia's dominance.
- Product Superiority: The launch of Gemini 3 has restored investor confidence in Google's ability to maintain a lead in the "AI Arms Race" against OpenAI and Anthropic.
Alphabet Market Capitalization Surge (Sept - Nov 2025)
| Date | Market Cap (Trillions USD) | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Oct 27, 2025 | $3.265 T | Pre-launch anticipation |
| Oct 30, 2025 | $3.409 T | Early rumors of TPU deals |
| Nov 18, 2025 | $3.650 T (Est) | Gemini 3 Launch |
| Nov 28, 2025 | $3.860 T | Pichai "25% Code" Announcement |
Table 1: Analysis of Alphabet's market cap growth correlated with key AI announcements.
2. Deconstructing "Vibe Coding": The New Paradigm of Production
Central to Pichai's recent commentary is his endorsement of a phenomenon known as "Vibe Coding." While the terminology may appear informal, it represents a fundamental abstraction in how humans interact with computing machines.
2.1 Defining the "Vibe"
The term was coined by Andrej Karpathy, a founding member of OpenAI and former Director of AI at Tesla, in February 2025. Karpathy described the practice as a state where the user "fully gives in to the vibes, embraces exponentials, and forgets that the code even exists".
In a B2B engineering context, Vibe Coding is the shift from imperative programming (telling the computer how to do something via syntax) to declarative intent (telling the computer what you want via natural language). The user focuses entirely on the functionality and user experience, delegating the implementation details—memory management, variable naming, library selection—to the Large Language Model (LLM).
2.2 The Spectrum of Vibe Coding
It is critical for CTOs to distinguish between the different "flavors" of this practice, as they carry vastly different risk profiles for the enterprise.
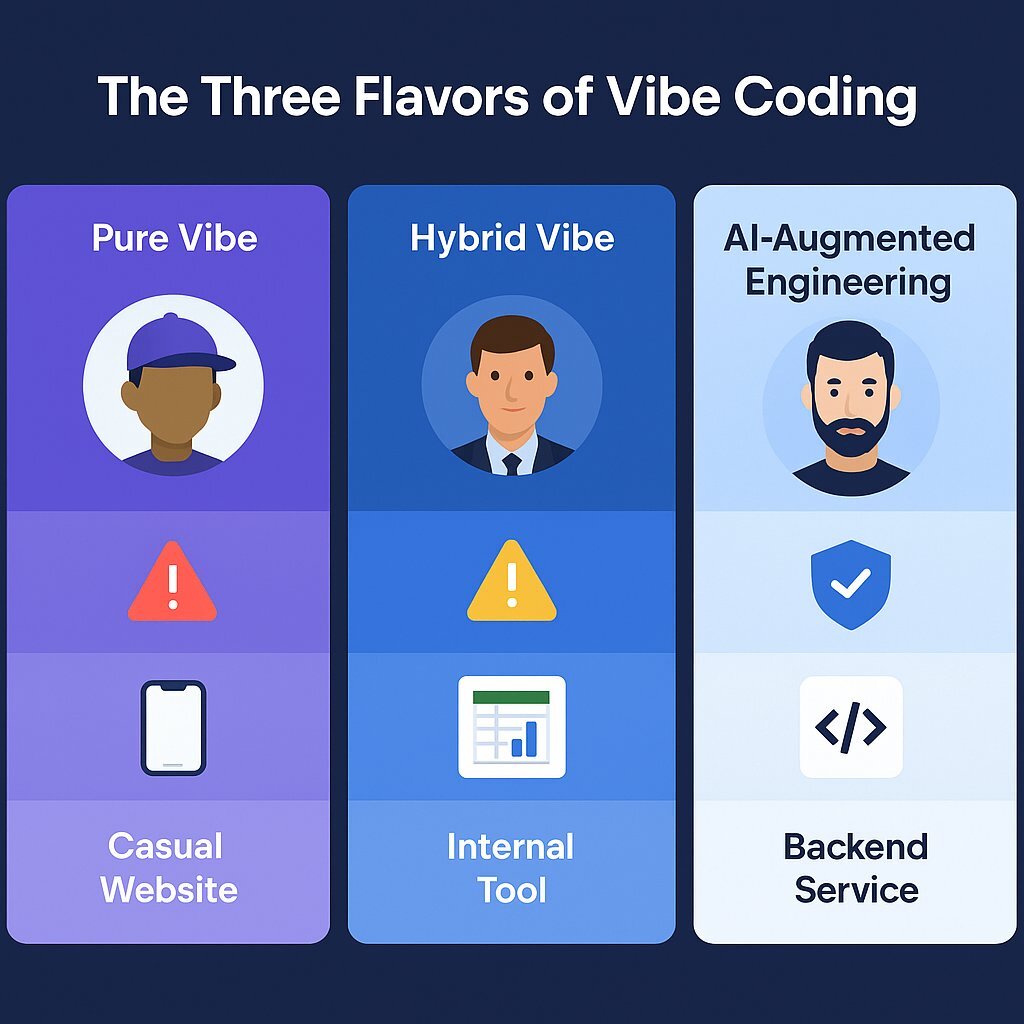
| Type | Definition | Primary User | Enterprise Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Vibe Coding | Trusting the AI output 100% without reviewing or understanding the code. "Forgetting the code exists." | Citizen Developers, Marketing, Sales | Extreme. High probability of security flaws, unoptimized logic, and shadow IT. |
| Hybrid Vibe Coding | Using AI to generate the bulk of the application, followed by a review of functionality (black-box testing) but not deep syntax. | Product Managers, Business Analysts | Moderate. Visual bugs are caught, but backend vulnerabilities (e.g., SQLi) may persist. |
| AI-Augmented Engineering | Professional developers using AI as a "pair programmer" (e.g., Cursor, Copilot) with deep line-by-line code review. | Software Engineers, DevOps | Managed. Risks are mitigated through CI/CD pipelines and expert oversight. |
2.3 The Democratization of App Development
Pichai noted that vibe coding has made software development "so much more enjoyable" and accessible to non-technical workers. This democratization is already transforming workplaces. HR professionals are building internal tools to track candidate pipelines; finance teams are scripting complex Excel automations using Python—all without writing a single line of traditional code.
Tools like Replit, Lovable, and Google's AI Studio are facilitating this shift, allowing users to build deployed applications via conversational prompts. For the "Innovative Marketing Director," this means the ability to spin up a landing page or a data analysis dashboard in minutes rather than waiting weeks for IT resources.
However, as we discuss in Section 4, this "Wild West" of ungoverned creation poses significant long-term risks regarding maintainability and security.
3. The Engine Behind the Shift: Gemini 3
The rapid acceleration of AI coding is powered by the next generation of foundation models. November 18, 2025, marked the launch of Gemini 3, Google's most advanced model to date. This release is not merely an iterative update; it represents a change in the cognitive architecture of the AI.

3.1 From Prediction to Reasoning
Unlike its predecessors (Gemini 1.0, GPT-3.5), which were primarily statistical text predictors, Gemini 3 is built as a reasoning engine. It features a new "Deep Think" capability, similar to OpenAI's o1 series, which allows the model to "pause" and deliberate before generating a response.
- Thought Signatures: The model generates internal "thought chains" to verify logic before outputting code. This significantly reduces "hallucinations" in complex logical tasks, such as architectural planning or debugging race conditions.
- Multimodal Fluency: Gemini 3 can analyze text, code, images, video, and audio simultaneously. A developer can upload a video screen recording of a bug occurring in a UI, and Gemini 3 can correlate that visual evidence with the underlying codebase to suggest a fix—a capability Pichai highlighted as a key differentiator.
- Agentic Capabilities: The model is designed for "agency." It can plan and execute multi-step workflows, such as "Analyze this entire repository, identify all deprecated API calls to the Stripe library, and submit individual pull requests to update them".
3.2 Benchmark Dominance: Gemini 3 vs. Claude 3.5 Sonnet
For much of 2024 and 2025, Anthropic's Claude 3.5 Sonnet was considered the "gold standard" for coding tasks due to its superior instruction following and large context window. However, early benchmarks and industry sentiment suggest Gemini 3 has usurped this position.
Comparative Analysis of Leading AI Coding Models (Nov 2025)
| Feature | Gemini 3 Pro | Claude 3.5 Sonnet | GPT-4o / o1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reasoning | Best in Class. "Deep Think" mode excels at complex logic puzzles and architectural design. | Strong, but lacks the dedicated "inference time compute" of Gemini's Deep Think. | Strong in o1, but slower and more expensive for general coding. |
| Context Window | 2 Million+ Tokens. Capable of ingesting entire repositories. | 200k - 500k Tokens. Good for modules, struggles with massive repos. | 128k Tokens. Limited for large-scale refactoring. |
| Multimodality | High. Can analyze video and audio natively for debugging. | Medium. Strong image analysis, no native video processing for code context. | Medium. Image analysis available. |
| Dev Sentiment | "The leap is insane." - Marc Benioff (Salesforce CEO). | Remains a favorite for "vibe" and creative writing tasks. | Losing ground in pure coding capability. |
The shift is palpable. Salesforce founder Marc Benioff publicly stated he switched from using ChatGPT daily to Gemini 3, citing the leap in reasoning and speed as "insane". For the "Visionary CTO," this signals a potential need to re-evaluate the underlying LLM providers in their corporate AI stack.
4. The Hidden Dangers: Security and Technical Debt
While Pichai’s "25% code" statistic is a triumph of efficiency, it is also a warning bell for security and quality assurance. As Baytech Consulting emphasizes in our "Tailored Tech Advantage" philosophy, speed without structural integrity is merely technical debt in disguise. The industry is currently facing a GenAI Code Security Crisis.
4.1 The Veracode 2025 Report: A Wake-Up Call
A comprehensive report by Veracode, analyzing code generated by over 100 LLMs in 2025, reveals startling statistics that every B2B executive must heed.
- The 45% Failure Rate: Nearly half (45%) of all AI-generated code samples contained insecure code that failed to meet basic security standards (OWASP Top 10).
- No "Smart" Safety: Crucially, the report found that newer, larger models (like Gemini 3 or GPT-4) were no better at writing secure code than smaller, older models. While they are better at syntax (making the code run), they are not better at security (making the code safe).
4.2 The "Java Problem" in Enterprise
For B2B firms relying on legacy stacks, the news is even more concerning. The report identified Java—the backbone of enterprise software, banking systems, and large-scale backends—as the riskiest language for AI generation.
- 72% Failure Rate: AI models generated insecure Java code 72% of the time.
- Why? LLMs are trained on the public internet (GitHub, StackOverflow). Much of the Java code available publicly is older, legacy code that predates modern security practices. The AI learns "patterns," and unfortunately, it has learned that hardcoding credentials or using weak encryption is a "standard" pattern in Java development.
Common Vulnerabilities in AI Code:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): 86% failure rate in defending against XSS. The AI frequently fails to sanitize user inputs.
- Log Injection: 88% failure rate. AI often writes raw user data directly into system logs, creating vectors for attack.
- Hardcoded Secrets: "Vibe coding" tools often inadvertently include API keys or passwords in the code snippets they generate, as they prioritize "getting it to work" over "configuration management".
4.3 The Rise of "Contextual Debt"
"Vibe Coding" creates a new, insidious form of technical debt.
- Traditional Tech Debt: "We wrote this quickly, we understand it, and we know we need to fix it later."
- Contextual Debt (AI Debt): "The AI wrote this. We don't fully understand how it works, so we are afraid to touch it."
Practitioners are already reporting "Vibe-Coded Messes"—spaghetti code that works for a prototype but is impossible to maintain, debug, or scale. If a non-technical marketing director builds a dashboard that becomes business-critical, and then that dashboard breaks, the IT team is left trying to reverse-engineer an AI's hallucinated logic.
5. Strategic Implementation: The "Human-in-the-Loop" Necessity
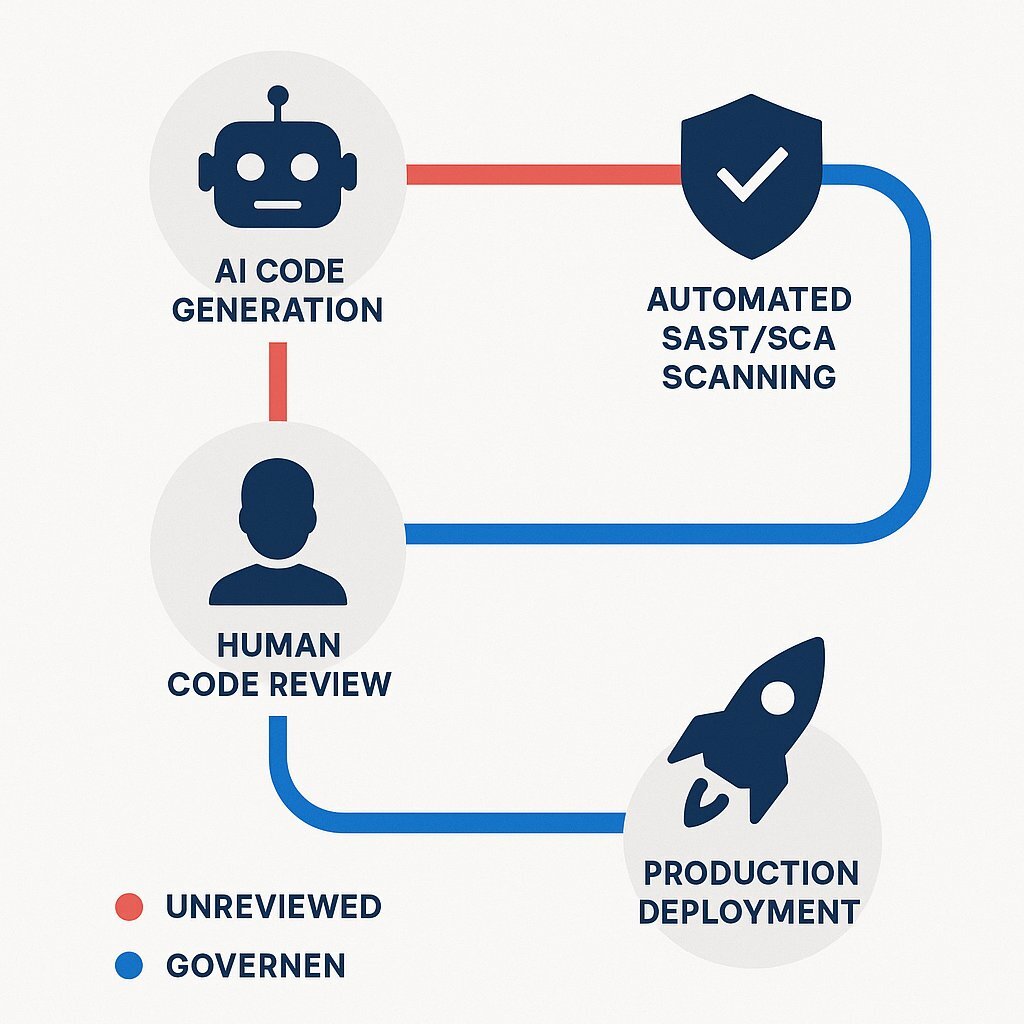
For B2B firms, the goal is not to ban AI coding—which would mean falling behind competitors like Alphabet who are moving 25% faster—but to govern it. The industry consensus for 2025 is the Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) approach.
5.1 The HULA Framework
Research recognized by ICSE 2025 introduces frameworks like HULA (Humans-in-the-loop LLM-based Agents), which emphasize that AI should act as an accelerator, not an autopilot. The workflow shifts from "Writing" to "Reviewing."
Best Practices for Enterprise Governance:
- Zero Trust for AI Code: Treat AI-generated code as "Untrusted Input." Just as you sanitize user data from a web form, you must sanitize code from an LLM. It must pass through the same rigor as external third-party libraries.
- Automated Guardrails: Human review is not enough (humans get tired). Implement automated Static Application Security Testing (SAST) and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) in the CI/CD pipeline. These tools can catch the 72% of Java errors that a human might miss during a "vibe" session.
- Architectural Observability: Use tools to monitor for "code drift." If an AI agent refactors a module, does it break the microservices architecture? Tools like vFunction or SonarQube are essential to maintain the "big picture" view that AI lacks.
- Bifurcated Access:
- Citizen Developers: Allowed to use "Vibe Coding" tools for internal, non-production, non-PII apps only.
- Engineering Teams: Must use "AI-Augmented" tools (VS Code extensions) with strict code review policies.
5.2 The Baytech Differentiator: Tailored Tech Advantage
At Baytech Consulting , we have integrated these realities into our delivery model. We leverage the velocity of tools like Gemini 3 to accelerate our Rapid Agile Deployment, but we wrap them in a layer of enterprise-grade rigor.
- Efficiency: We use AI to generate boilerplate, unit tests, and documentation, freeing our highly skilled engineers to focus on complex business logic and architecture.
- Quality: Every line of AI code is reviewed by a human expert. We do not "vibe code" critical infrastructure.
- Transparency: We provide clients with the assurance that their "Tailored Tech" is built by engineers who understand the code, not just an algorithm that guessed it.
6. Future Outlook: 2025 - 2028
The trend lines drawn by Gartner and McKinsey paint a picture of rapid adoption and shifting roles.
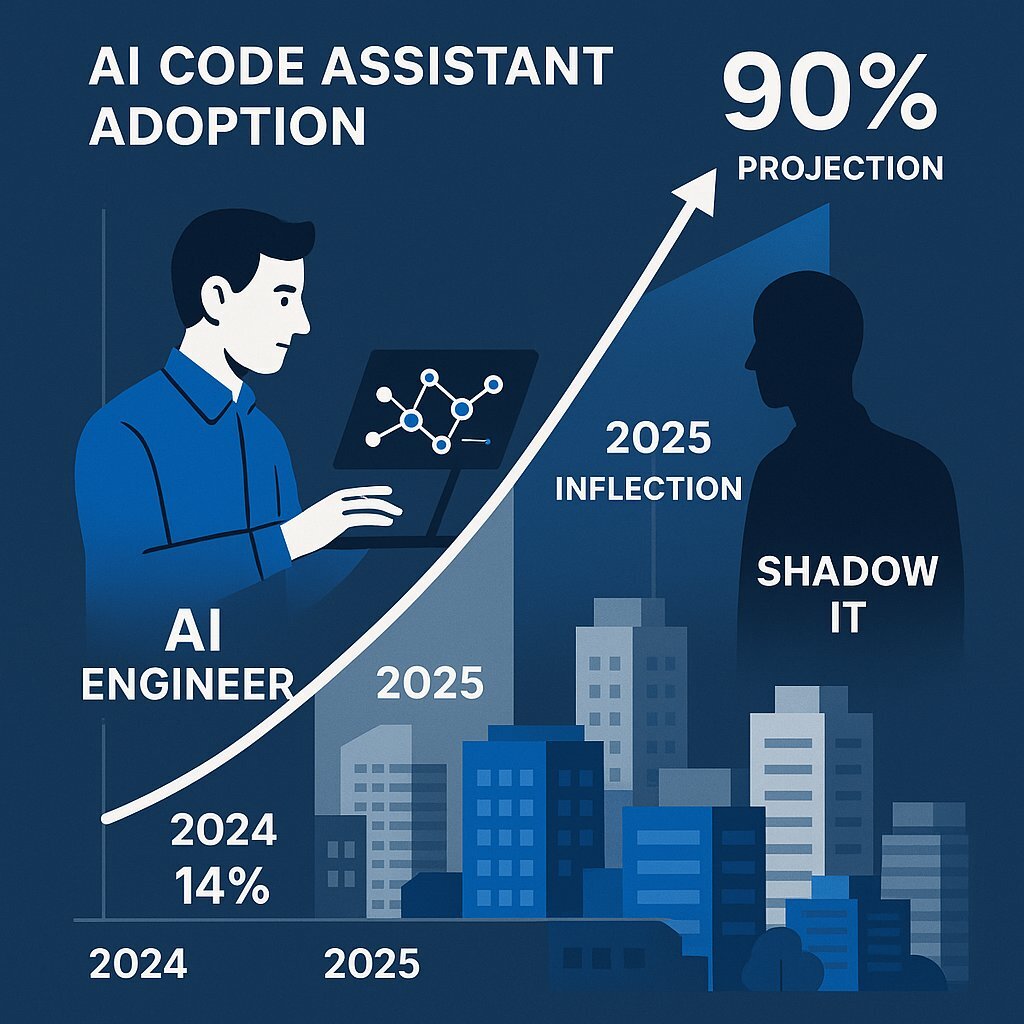
- 90% Adoption by 2028: Gartner predicts that 90% of enterprise software engineers will use AI code assistants by 2028, up from less than 14% in early 2024.
- The Rise of the "AI Engineer": The role of the developer is shifting from "writing syntax" to "orchestrating agents." The most valuable skill in 2026 will not be memorizing the Java standard library, but the ability to guide an AI agent to a secure, scalable solution.
- Shadow IT Explosion: By 2028, 40% of new production software will be created using vibe coding techniques by non-technical staff. CIOs must prepare for a massive expansion of the software estate that sits outside traditional IT control.
7. Conclusion: How to Navigate the AI Coding Era
Sundar Pichai’s revelation that AI writes 25% of Google’s code is more than a statistic; it is a signal that the fundamental economics of software production have changed. The efficiency gains are real, attainable, and massive. However, the accompanying rise of "vibe coding" and the verified security vulnerabilities in AI-generated code present a complex challenge for B2B executives.
Key Takeaways for the C-Suite:
- Embrace the Velocity: You cannot compete if your competitors are shipping 25% faster. Adopt AI tools, but do so strategically.
- Reject the Hype of "No-Code" for Core Systems: "Vibe coding" is excellent for prototyping but dangerous for production. Ensure your core IP is built by engineers who understand the code, not just the "vibe."
- Fortify Your Governance: Implement strict "Human-in-the-Loop" protocols. Use automated security scanning to catch the "Java Problem" and other AI-induced vulnerabilities.
Actionable Advice:
- For the CTO: Audit your team's use of AI. Implement a "Zero Trust" policy for AI-generated code in your CI/CD pipeline. Evaluate Gemini 3 for its reasoning capabilities in complex refactoring.
- For the CFO: Expect initial spikes in cloud costs or "token" usage as teams experiment. Balance this against the long-term reduction in technical debt if managed correctly.
- For the CEO: Look for partners, like Baytech Consulting, who combine the speed of AI with the safety of US-based, senior engineering talent.
Supporting Articles
- https://www.veracode.com/blog/genai-code-security-report/ – Veracode's deep dive into the 45% failure rate of AI code.
- https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2025-07-01-gartner-identifies-the-top-strategic-trends-in-software-engineering-for-2025-and-beyond – Analysis of the shift toward AI-native engineering.
- https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-3/ – Official overview of the capabilities powering Google's transformation.
Frequently Asked Question
Q: If AI writes 25% of the code, does that mean I can reduce my engineering headcount by 25%?
A: No. In fact, attempting to do so could be catastrophic for your software's long-term health.
While AI accelerates the writing of code (typing syntax), it significantly increases the need for reviewing, debugging, and securing that code. As the Veracode report highlights, AI-generated code is prone to security flaws (45% failure rate) and maintainability issues.
Think of AI as a hyper-productive junior developer. It can produce massive amounts of output, but it lacks wisdom, context, and security awareness. You need your senior engineers more than ever to act as architects and reviewers—the "Human in the Loop"—to ensure that the "25% of code" written by AI doesn't turn into 100% technical debt. The efficiency gain should be reinvested into faster feature delivery and higher quality, not headcount reduction. Companies that cut senior talent in favor of AI generation often find themselves stalled months later by unmanageable "Vibe-Coded Messes."
This shift highlights why, even with enterprise AI coding tools, the increasing reliance on automation actually amplifies the critical need for skilled human expertise—rather than replacing it. Leaders must strike a careful balance between automated efficiency and hands-on review.
To succeed in the AI-augmented era, risk management and robust governance must go hand-in-hand with adoption. Unchecked "vibe coding" creates opportunities for attackers; instead, organizations should review how AI-driven tools like CodeMender are revolutionizing software security—with an emphasis on human oversight.
Further, as you bring these emerging AI workflows into your business, don't overlook the foundation: successful software project management ensures that agile and DevOps practices remain robust amid rapid generative development cycles.
As security challenges mount and authentication grows more complex, especially in AI-powered and SaaS environments, explore how strategic hybrid authentication strategies can protect user data and ensure compliance in a distributed, AI-enhanced business world.
Importantly, diligent software scoping remains indispensable for controlling costs, maximizing ROI, and heading off technical debt before it starts—especially in an era when AI can generate code at speed. Learn more in our guide to mastering software scoping for project success.
Finally, for entrepreneurs and product teams stepping into this fast-moving landscape, the guidance of an expert startup consultant can add lasting value. From strategic planning to robust AI integration, the right partner helps you navigate the tradeoffs and opportunities of the modern software economy.
About Baytech
At Baytech Consulting, we specialize in guiding businesses through this process, helping you build scalable, efficient, and high-performing software that evolves with your needs. Our MVP first approach helps our clients minimize upfront costs and maximize ROI. Ready to take the next step in your software development journey? Contact us today to learn how we can help you achieve your goals with a phased development approach.
About the Author

Bryan Reynolds is an accomplished technology executive with more than 25 years of experience leading innovation in the software industry. As the CEO and founder of Baytech Consulting, he has built a reputation for delivering custom software solutions that help businesses streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth.
Bryan’s expertise spans custom software development, cloud infrastructure, artificial intelligence, and strategic business consulting, making him a trusted advisor and thought leader across a wide range of industries.


