
How Will AI Really Affect Your Operations and People?
July 18, 2025 / Bryan Reynolds
Introduction: Moving from AI Anxiety to AI Strategy
The conversation around Artificial Intelligence is trapped between two extremes. On one side, there's the utopian hype promising a work-free world of automated abundance. On the other, there's the dystopian fear of mass unemployment and rogue algorithms. For a B2B leader trying to navigate the complexities of the modern market, neither of these narratives is particularly useful. The real challenge—and the real opportunity—lies in cutting through this noise to build a clear, pragmatic strategy based on what AI can actually do for your business, your operations, and your people, right now.
This leads to the critical questions that are likely on your mind: "Will AI replace my team? What new skills will they need to survive and thrive? And how, specifically, can this technology make my business more efficient and competitive?"
This guide is designed to provide honest, transparent answers to those exact questions. We will move beyond the headlines and into the data, drawing from authoritative reports and real-world case studies to build a practical framework for AI adoption. The central argument is this: AI's primary role in the enterprise is not replacement, but augmentation . It is a profoundly powerful tool that, when wielded correctly, enhances human capability, frees your team from low-value work, and drives unprecedented operational efficiency. This isn't just another technology trend; it's a fundamental strategic shift.
At Baytech Consulting, our philosophy has always been that technology should provide a Tailored Tech Advantage , not a one-size-fits-all problem. True competitive differentiation comes from custom-crafting solutions to solve your unique challenges. This article will provide the strategic lens you need to think about that tailored advantage, covering three critical areas:
- The People Question: The truth about AI's impact on jobs and the new human-AI partnership.
- The Skills Imperative: The specific capabilities your team will need in an AI-powered world.
- The Operations Engine: How AI streamlines processes and supercharges growth, from the back office to the sales frontline.
Let's move from AI anxiety to AI strategy.
The People Question: Will AI Replace Our Employees?
The fear of job displacement is the single greatest concern surrounding AI adoption, and for good reason. Stories of AI replacing writers, artists, and coders fuel a narrative of obsolescence. However, a closer look at the data and the nature of work itself reveals a more nuanced and ultimately more optimistic picture. The conversation isn't about replacement; it's about a radical redesign of work itself.
The Honest Answer: It's About Task Automation, Not Job Obliteration
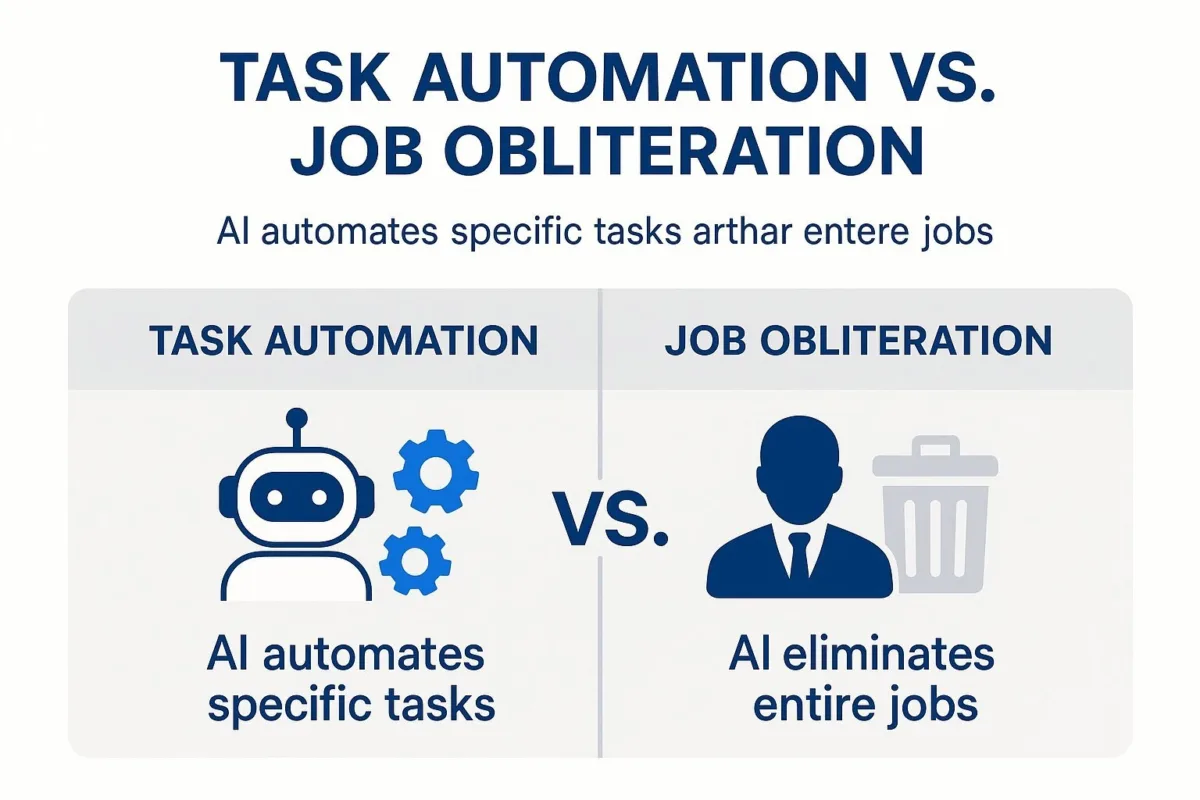
The most critical concept to grasp is the distinction between a "job" and a "task." A job is a human-defined construct, a collection of various tasks and responsibilities. AI, particularly in its current form, doesn't automate entire jobs; it automates specific, repetitive, and often data-heavy tasks within those jobs.
Deloitte analysis clarifies this by breaking work into three categories: tasks humans do better (requiring creativity, empathy, complex problem-solving), tasks machines do better (data processing, pattern recognition, repetition), and a rapidly growing category of tasks best done through human-machine collaboration. This collaborative model is already the norm. A World Economic Forum report highlights that in today's workplace, 47% of tasks are performed primarily by humans, 22% by technology, and a significant 30% involve a collaborative effort. AI is simply accelerating a trend that is already well underway.
The New Paradigm: Augmentation and the "Human-in-the-Loop"
Instead of seeing AI as a replacement, it's more accurate to view it as a "copilot" or a "supertool" that augments and amplifies human capabilities. This idea has been termed "Superagency" by McKinsey—a state where individuals, empowered by AI, can supercharge their creativity, productivity, and impact. An employee with an AI assistant can analyze data faster, generate initial drafts in seconds, and identify market trends that would have been invisible before. They become more, not less, valuable.
The practical application of this philosophy is the Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) model. HITL is a collaborative approach where humans are intentionally integrated into the AI lifecycle to guide, verify, and refine its outputs. In a HITL system, an AI might draft a sales proposal, but a human sales director reviews and refines it. An AI might flag a potentially fraudulent transaction, but a human analyst makes the final call. This partnership is essential for several reasons:
- It mitigates bias: AI models trained on biased data will produce biased results. Human oversight is critical to catch and correct these biases.
- It ensures accuracy: AI models can "hallucinate" or produce factually incorrect information. Human verification is the final line of defense against costly errors.
- It builds trust: For high-stakes B2B decisions, a "black box" AI is unacceptable. HITL provides the transparency and accountability needed for leaders to trust and act on AI-generated insights.
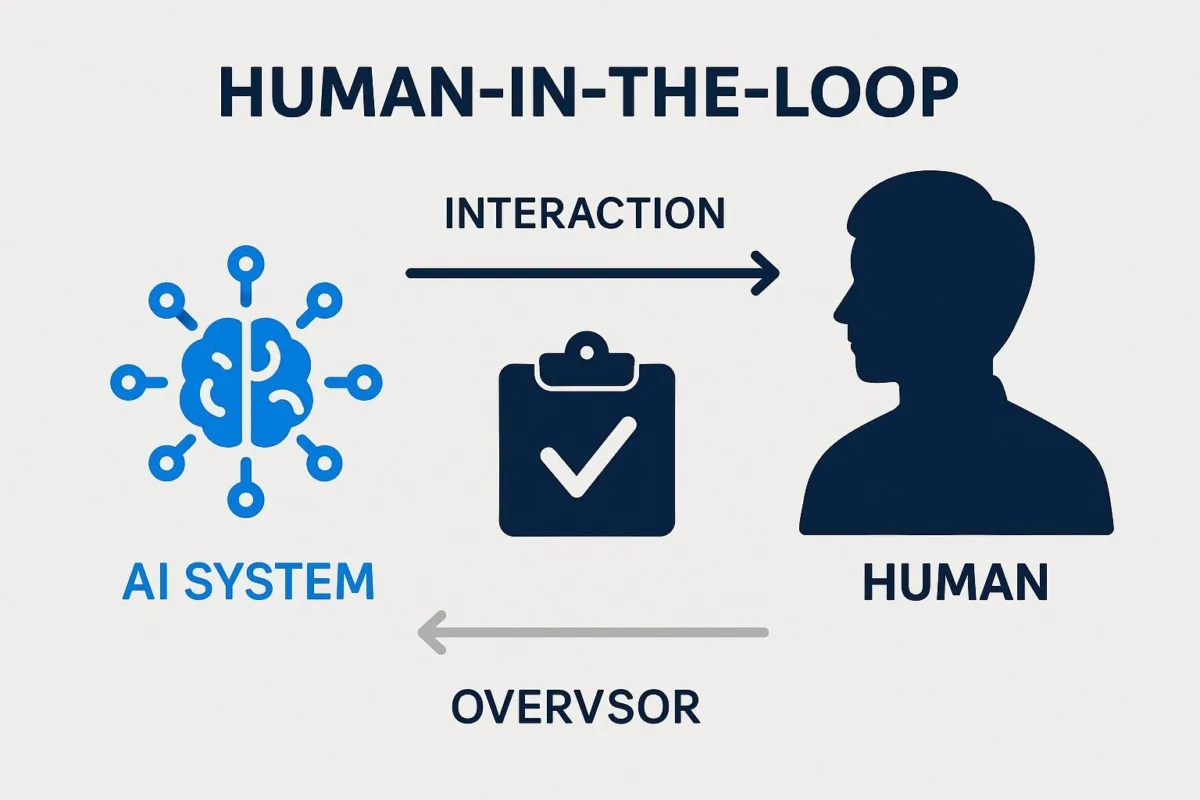
This approach ensures that AI serves as a tool for human empowerment, not a replacement for human judgment.
What the Data Says About the Future of Jobs
The most definitive data on this topic comes from the World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report . It projects that while automation and AI may displace 85 million jobs globally by 2025, they are simultaneously expected to create 97 million new roles . This results in a net gain of 12 million jobs, fundamentally shifting the narrative from one of job loss to one of profound job evolution and redistribution.
Of course, this transition won't be frictionless. Certain roles, especially those involving routine content creation or coding, are experiencing real disruption. Recent studies show a measurable decrease in job postings for writing and creative roles following the introduction of powerful generative AI tools. This honesty is crucial; while the macro picture is positive, the impact on specific professions can be significant and requires proactive management.
This leads to a critical realization for any business leader. The most immediate threat is not that your employees will be replaced by an algorithm. The real danger is that your competitor will adopt AI to augment their workforce, achieving a level of speed, insight, and operational efficiency that your un-augmented team simply cannot match. A technical writer who can produce twice as many high-quality articles with an AI assistant makes their less-efficient peers obsolete. A sales team that uses AI to perfectly time their outreach will consistently outperform a team relying on intuition alone.
Therefore, the strategic question for leaders must evolve. It is no longer, "How do I protect my people from AI?" It is now, "How do I empower my people with AI to dominate our market?" This reframes AI adoption from a defensive, cost-cutting measure into an offensive, growth-oriented strategy.
To make this tangible, consider how augmentation transforms common B2B roles:
| Role | Repetitive Tasks Automated by AI | Augmented Strategic Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Head of Sales | Generating weekly pipeline reports, manual CRM data entry, drafting initial outreach emails. | Coaching sales team on AI-identified negotiation tactics, developing strategy based on predictive sales forecasts, focusing on high-value relationship building. |
| CFO / Finance | Manual invoice processing, expense report categorization, pulling data for standard financial reports. | Modeling complex financial scenarios with predictive analytics, identifying cost-saving opportunities from AI-driven operational analysis, focusing on strategic capital allocation. |
| Marketing Director | A/B testing ad copy variants, scheduling social media posts, compiling campaign performance data. | Developing overarching campaign strategy based on AI-driven microsegmentation, analyzing deep market trends surfaced by AI, focusing on creative brand building. |
| CTO / Tech Lead | Routine code debugging, writing boilerplate code, monitoring server status for standard alerts. | Architecting scalable AI infrastructure, designing proprietary AI models to solve unique business problems, leading the company's overall technology strategy. |
The Skills Imperative: What New Capabilities Will Your Team Need?
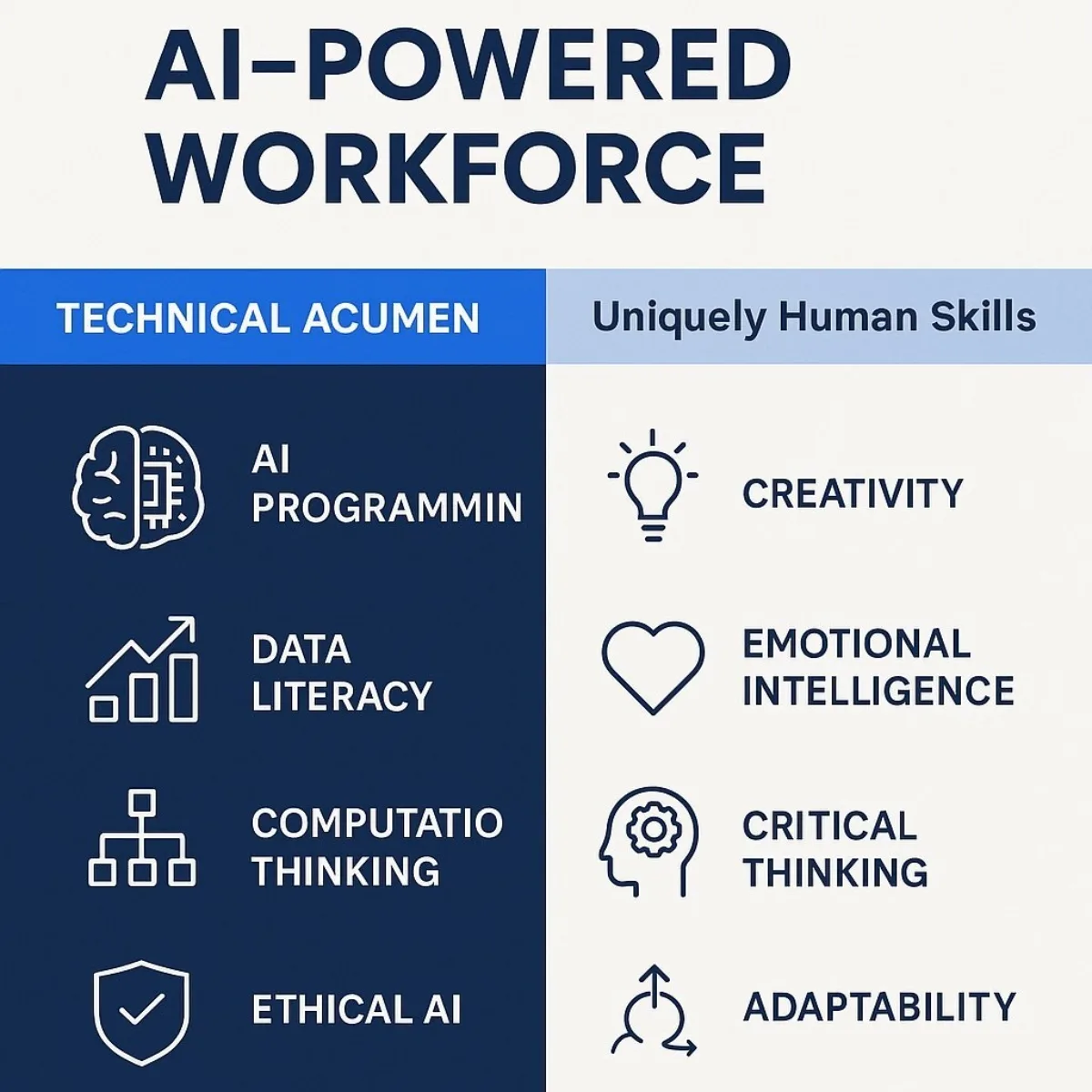
The integration of AI into the workplace isn't just a technological upgrade; it's a catalyst that creates an urgent and significant skills gap. Simply deploying AI tools without preparing your workforce is a recipe for failure. The organizations that will win in the coming decade are those that strategically invest in reskilling their teams, focusing on a dual-pronged approach: building a new baseline of technical literacy while simultaneously doubling down on the "uniquely human" skills that AI cannot replicate.
The Two Halves of the AI-Ready Skillset
The future-proof employee will possess a blend of technical competence and deep human-centric abilities.
Technical Acumen: The New Baseline
This is not about turning your entire marketing department into machine learning engineers. It's about establishing a new, universal level of digital fluency that allows every employee to work effectively alongside AI. Key areas include:
- AI Literacy: A foundational understanding of how AI works, its core capabilities (e.g., pattern recognition, content generation), and, crucially, its limitations (e.g., lack of true understanding, potential for bias). This is rapidly becoming a non-negotiable skill; a recent LinkedIn report found that hiring managers are already over 50% more likely to favor candidates with AI literacy skills. For a comprehensive overview of how AI is transforming the modern workplace and what leaders need to know, see our analysis of the state of artificial intelligence in 2025.
- Prompt Engineering: The ability to craft clear, concise, and effective instructions to guide generative AI tools toward a desired output. While some predict this skill will become less critical as AI becomes more intuitive and user-friendly, for the foreseeable future, knowing how to "talk" to an AI is a key differentiator for productivity. If you're looking to sharpen your team's skills in this area, check out our guide to maximizing the utility of ChatGPT for practical tips and advanced prompting techniques.
- Data Analysis & Critical Thinking: The capacity to not just consume AI-generated reports and insights, but to critically evaluate them. This means questioning the underlying data, identifying potential anomalies, and using the AI's output as a starting point for deeper human analysis, not an endpoint.
Uniquely Human Skills: The New Premium
Herein lies the great paradox of the AI era: the more we integrate advanced technology into our work, the more valuable our core humanity becomes. AI can process data at a scale no human can, but it cannot replicate the nuanced skills that drive true innovation and leadership. As AI automates routine cognitive tasks, the following human skills will command a premium:
- Complex Problem-Solving: AI is excellent at solving problems it has been trained on. Humans, however, excel at solving novel, unexpected problems that fall outside the training data. The ability to think critically, question assumptions, and devise creative solutions to new challenges will be indispensable.
- Creativity & Innovation: While AI can generate startlingly good text, images, and code, it is fundamentally remixing patterns from its training data. True, out-of-the-box creativity—the kind that leads to a breakthrough product, a disruptive business model, or a game-changing marketing campaign—remains a uniquely human domain.
- Emotional Intelligence & Communication: Skills like empathy, persuasion, leadership, and collaboration cannot be coded. In a workplace where technology handles more of the analytical heavy lifting, the ability to motivate a team, negotiate a complex deal, and build strong client relationships becomes even more critical.
A Leader's Roadmap to Reskilling and Fostering a Culture of Learning
Addressing the skills gap requires a deliberate, top-down strategy. Here are four actionable steps for executives:
- Conduct a Skills Audit: Begin by mapping the current skills of your workforce. Then, identify the future skills that will be required to execute your business strategy in an AI-augmented environment. This gap analysis will be the foundation of your training plan.
- Invest in Targeted Training: Look to the models of large corporations like Microsoft, which have initiated global skills programs to bring digital competencies to millions. This investment should be continuous and multifaceted, including formal workshops, access to online courses (like those on EdX or Coursera), and hands-on pilot programs with new AI tools.
- Foster a Culture of Lifelong Learning: In the age of AI, skills have a shorter half-life than ever before. Learning can no longer be confined to one's early career. Leaders must champion and model a culture of curiosity, experimentation, and continuous professional development.
- Empower Your Champions: A recent McKinsey report found that millennials are often the most experienced and enthusiastic AI users in an organization. Identify these internal "AI optimists," who are often already in management roles, and empower them. Give them the tools, training, and authority to become advocates for change, training their peers and demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI in their daily work.
Thinking about this strategically reveals a powerful truth. As AI foundation models become more powerful and their costs plummet, access to the technology itself will cease to be a competitive advantage. It will become a commodity, like electricity or cloud computing. The true, durable competitive moat will not be built on having AI, but on having a workforce that can uniquely and effectively leverage that AI to create value. A highly skilled, AI-augmented team is a proprietary asset that is far more difficult for a competitor to replicate than simply purchasing a software license. From this perspective, a leader should view their reskilling budget not as a line-item expense, but as a strategic investment in building a defensible, long-term market advantage.
The Operations Engine: How Can AI Drive Unprecedented Efficiency?

For B2B leaders, the promise of AI-driven operational efficiency is often the most compelling reason for adoption. This isn't just about incremental cost savings or marginal productivity gains. It's about a transformative force that can reclaim thousands of hours of human potential from low-value, repetitive work, enabling a fundamental shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive, data-driven, and highly strategic operations.
Core AI Use Cases for B2B Operations (with Real-World Examples)
AI is already re-architecting the core functions of businesses across industries, from finance and manufacturing to healthcare and logistics. If you're curious how these real-world applications are reshaping business models, our in-depth article on AI-enabled software development dives deeper into practical use cases and the evolving role of the developer.
- Intelligent Automation: This goes far beyond basic Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Modern AI can understand and process unstructured data, leading to staggering efficiency gains. A landmark example is JPMorgan Chase's COiN platform , which uses AI to review and interpret complex commercial credit agreements. It can process 12,000 contracts in mere seconds—a task that previously consumed 360,000 human work-hours annually. In the tech sector, AI-powered tools provide intelligent code completion and automated code reviews, catching bugs early and accelerating development cycles, freeing up highly-paid engineers to focus on innovation instead of maintenance.
- Predictive Analytics for Resource Management: AI excels at optimizing the use of both physical and human assets.
- In Retail and Supply Chain, giants like Amazon and Walmart use AI-powered analytics to track inventory in real-time and forecast demand with incredible accuracy, drastically reducing waste and preventing costly stockouts.
- In Manufacturing, companies deploy AI for predictive maintenance, analyzing sensor data from machinery to predict potential failures before they happen. This proactive approach minimizes expensive downtime and extends the life of critical assets.
- In Healthcare, providers like the Cleveland Clinic have used AI to optimize patient scheduling, staff deployment, and bed allocation. This not only improves patient outcomes but also helped the organization offset rising costs and achieve a budget surplus.
- Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization: AI is the central nervous system of the modern supply chain. It optimizes delivery routes by analyzing real-time traffic, weather patterns, and historical data to reduce fuel costs and delays. In warehouses, Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) powered by AI navigate floors, pick items, and deliver them to packing stations with a speed and precision that humans cannot match, dramatically shortening order fulfillment times.
A Deep Dive for Growth Leaders: AI for Sales and Lead Generation

For Heads of Sales and Marketing Directors, AI is not just an operational tool; it's a revenue-generating engine that can reshape the entire customer acquisition funnel. Companies using AI for lead generation report, on average, a 50% increase in conversions and a 40% reduction in customer acquisition costs. For an analysis of the evolving CRM landscape—and whether custom or off-the-shelf solutions offer the best fit for AI-powered sales—read our comprehensive guide to custom CRM development.
- Finding and Qualifying Leads with Surgical Precision: The days of cold calling a massive, undifferentiated list are over. AI fundamentally changes how leads are identified and prioritized.
- Predictive Lead Scoring: AI analyzes thousands of data points—website behavior, email engagement, firmographics, social media activity, and third-party intent data—to assign a score to each lead based on their likelihood to convert. This allows sales teams to stop wasting time on low-potential prospects and focus their energy exclusively on those ready to buy. B2B companies using these strategies have reported lead conversion rates increasing by over 50%.
- Case Study: Harley-Davidson. The iconic motorcycle brand faced a challenge in attracting the right customers in a niche market. By implementing an AI-powered lead generation tool that analyzed demographic data and online engagement, they were able to increase qualified leads from 1 per day to 40 per day in the first month, boosting overall sales by nearly 30% in key markets.
- Hyper-Personalization at Scale: B2B buyers expect tailored, relevant interactions. Generative AI makes this possible at a scale that was previously unimaginable. It can craft highly personalized outreach emails, ad copy, and marketing content that speaks directly to specific microsegments, buyer personas, or even individual pain points.
- Case Study: Fortune 100 Financial Services Firm. By partnering with IBM and using Salesforce Marketing Cloud, this organization implemented an AI-driven strategy for increased segmentation and personalization. The result was a 3-5% improvement in target conversion—a massive impact at their scale.
- Optimizing the Sales Process Itself: AI acts as a coach and an assistant for the entire sales team.
- Conversation Intelligence: Tools like Gong.io record and analyze sales calls, using AI to identify the language, tactics, and questioning strategies used by top-performing reps. These insights are then used to provide real-time coaching and feedback to the entire team, lifting everyone's performance.
- Sales Rep Augmentation: In a case study with Takeda Oncology , AI models provided sales reps with bi-weekly updates, contextually relevant messages to share with customers, and even recommended treatment choices to discuss with healthcare providers, enabling more informed and effective conversations.
The long-term impact of AI on operations extends far beyond simply making existing processes more efficient. Initially, a company might use AI to automate invoicing, which is a form of process optimization . However, as AI becomes more deeply integrated, it enables entirely new capabilities. A logistics company like UPS or a manufacturer like BMW can build a "digital twin"—a complete virtual replica of its entire supply chain or factory floor—to run thousands of simulations and optimize distribution in ways previously impossible. An advertising company can move beyond static billboards to create dynamic ones that change their messaging in real-time based on neighborhood data, as PODS did with their "World's Smartest Billboard" campaign.
This is the shift from optimization to business model innovation . The logistics company is no longer just selling the movement of boxes; it's selling predictive supply chain intelligence as a service. This is where the true transformative power of AI lies, and it's where a partnership with a custom software development firm like Baytech Consulting becomes invaluable. Off-the-shelf software can help with optimization, but building a proprietary, data-driven business model requires the Tailored Tech Advantage of a custom-built application. For more on how custom digital solutions can help you outpace the competition, see our report on leveraging custom software for sustainable growth.
The Implementation Playbook: A Practical Guide to AI Adoption
Embarking on an AI journey can feel daunting. The technology is complex, the costs are perceived as high, and the risk of failure is real. However, successful AI implementation is not about a "big bang" organizational overhaul. It's a strategic, phased approach that begins with clear business objectives and prioritizes data readiness, agile execution, and measurable return on investment.
The "Big Five" of AI Implementation: Answering Your Toughest Questions
For any executive considering an AI initiative, five key questions inevitably arise: How much will it cost? What can go wrong? How do we compare options? What do customers say? And what's the best way to do it? Let's tackle the most critical of these head-on.
Pricing: What Does AI Actually Cost?
Providing a single price for "AI" is impossible, as it ranges from simple software subscriptions to massive, multi-year transformation projects. The high cost of implementation is a significant barrier to entry for many businesses. To bring clarity, it's helpful to think in tiers:
- Tier 1: Off-the-Shelf & SaaS Tools: This includes AI-enhanced CRM platforms, marketing automation tools, and generative AI content creators. These are typically subscription-based and can range from $50 to $500 per month per user . For a deeper understanding of the hidden costs and long-term trade-offs of off-the-shelf versus custom software, explore our analysis of the hidden costs of offshore software development.
- Tier 2: Mid-Sized Custom Projects: This involves building a specific solution to a specific problem, such as a predictive analytics model for lead scoring or a custom Natural Language Processing (NLP) application for document analysis. These projects typically range from $100,000 to $500,000 .
- Tier 3: Enterprise-Grade Systems: This is the realm of large-scale, mission-critical systems, such as developing a proprietary Large Language Model (LLM), an autonomous supply chain platform, or a company-wide "digital twin." These investments can range from $500,000 to over $10 million .
The primary cost drivers behind these figures are threefold:
- Data: Acquiring, cleaning, labeling, and storing the vast amounts of high-quality data needed to train AI models is a significant expense.
- Infrastructure: AI workloads are computationally intensive, requiring specialized hardware like GPUs. Businesses must choose between the high upfront capital expenditure of on-premise servers or the recurring operational expense of cloud computing platforms like Azure or AWS. To learn more about choosing the right infrastructure for your needs, check out our analysis of private vs. public cloud for mid-market companies.
- Talent: The demand for skilled AI professionals far outstrips the supply. Salaries for experienced data scientists and machine learning engineers can easily range from $100,000 to over $300,000 annually.
This table provides a framework for budgeting and understanding the relationship between cost and business application.
| Implementation Tier | Estimated Cost Range | Typical B2B Use Cases | Primary Cost Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1: Off-the-Shelf SaaS | $500 - $5,000 / month | AI-powered chatbots, content generation tools (e.g., Jasper), AI features in existing CRM (e.g., Salesforce Einstein). | Subscription fees, per-user licenses. |
| Tier 2: Custom Pilot Project | $50,000 - $250,000 | Custom predictive lead scoring model, automated document analysis tool, targeted fraud detection system. | Developer/consultant hours, data annotation services, initial cloud compute costs. |
| Tier 3: Enterprise System | $500,000+ | Proprietary LLM for internal knowledge management, custom supply chain digital twin, autonomous operations platform. | Specialized talent acquisition, large-scale GPU compute infrastructure, extensive data engineering, ongoing maintenance. |
Problems: Navigating the Common Pitfalls
Many AI initiatives fail, and usually for the same set of predictable reasons. Understanding these pitfalls is the first step to avoiding them.
- Data Quality & Availability: This is the number one killer of AI projects. AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. If your data is fragmented across disparate systems, inconsistent, incomplete, or biased, your AI will produce unreliable or incorrect results. A staggering one-third of AI programs fail due to data-related challenges. For expert advice on transforming your organization's data entry and accuracy, see our latest guide to eliminating data entry errors and maximizing efficiency.
- Integration with Existing Systems: AI tools do not operate in a vacuum. They must be seamlessly integrated with your existing CRM, ERP, and other operational platforms. This is a major hurdle, especially for companies with legacy systems or a patchwork of off-the-shelf software that doesn't communicate well. This is precisely where a Tailored Tech Advantage from a custom development partner like Baytech becomes critical, as we build solutions designed to integrate with your specific tech stack, avoiding the rigidity and vendor lock-in of pre-packaged software.
- Security & Compliance: AI systems often process sensitive customer and proprietary data, creating significant security and privacy risks. Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is paramount, and requires robust security measures to prevent costly data breaches.
- The "Black Box" Problem & Bias: The inner workings of some complex AI models can be opaque, making it difficult to understand why they reached a certain conclusion. This "black box" nature erodes trust and can be a compliance nightmare. Furthermore, if not carefully managed, AI can amplify existing human biases present in the training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in areas like hiring or lending. This reinforces the absolute necessity of explainable AI and Human-in-the-Loop oversight. To understand the risks of AI "hallucinations" and practical steps for minimizing them, read our deep dive on hidden dangers of AI hallucinations in financial services.
Best Practices: A Strategic Framework for AI Adoption
Instead of a random walk, leaders need a strategic framework to decide where to apply AI. A powerful model comes from a 2025 Stanford-led research paper that maps tasks onto a Desire-Capability Landscape . This framework, based on surveys of over 1,500 workers and AI experts, divides potential AI applications into four zones based on worker desire for automation and current AI capability :
- Automation "Green Light" Zone (High Desire, High Capability): This is the low-hanging fruit. These are repetitive, low-value tasks that workers want to offload and that current AI can handle reliably. This zone is perfect for initial pilot projects to build momentum, demonstrate quick ROI, and get your team comfortable with the technology. Example: Automating the categorization of expense reports.
- Automation "Red Light" Zone (Low Desire, High Capability): This zone requires extreme caution. These are tasks that AI can do, but that workers feel require significant human judgment, creativity, or ethical consideration. Deploying full automation here can destroy morale and lead to poor outcomes. The best approach is a Human-in-the-Loop system where AI can assist or suggest, but a human makes the final decision. Example: Making final hiring decisions or setting high-level company strategy.
- R&D Opportunity Zone (High Desire, Low Capability): This is where the biggest competitive advantages are built. These are complex, high-value problems that workers desperately want help with, but that off-the-shelf AI tools cannot yet solve. They are often unique to your business or industry. This zone is the sweet spot for partnering with a custom software development firm like Baytech Consulting to build a proprietary AI solution that gives you a durable market edge. Example: Building a custom model to predict customer churn based on your unique product usage data.
- Low Priority Zone (Low Desire, Low Capability): These are tasks that workers don't want to automate and that AI isn't good at anyway. Ignore these areas and focus your resources elsewhere.
Your First 90 Days: An Agile Approach to Getting Started
The best way to begin is not with a massive, multi-year plan, but with an agile, iterative approach that delivers value quickly. This aligns perfectly with Baytech's Rapid Agile Deployment methodology. For more on our process and how we blend Agile methodology with AI implementation, visit our services page.
- Days 1-30: Identify a High-Impact Business Problem. Don't start with the technology. Start with a real business pain point. Is your lead qualification process too slow? Is your team drowning in manual data entry? Map this problem to the four-zone framework to determine the right approach.
- Days 31-60: Launch a Small-Scale Pilot Project. Select a well-defined project, ideally from the "Green Light" zone or a high-potential "R&D Opportunity" zone. Define clear, measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for success. What outcome are you trying to achieve? (e.g., "Reduce lead qualification time by 50%," "Automate 80% of invoice processing.")
- Days 61-90: Train the Team & Measure ROI. Involve the end-users of the AI tool from the very beginning. Provide them with the necessary training and support. At the end of the 90 days, rigorously measure your pilot's performance against the KPIs you set.
- Iterate and Scale: Use the learnings from your successful pilot to inform the next project. Celebrate the win and build on that momentum, gradually scaling AI initiatives across the organization in a way that is driven by proven value, not by hype.
Conclusion: Your Future is Human-Led and AI-Powered
The central question for every B2B leader is not if AI will transform their business, but how they will choose to lead that transformation. The evidence is clear: the narrative of mass replacement is a distraction from the real, and far more exciting, story of augmentation and empowerment. The most successful, resilient, and dominant companies of the next decade will be those that see AI not as a threat to be managed, but as a powerful tool to unleash their greatest asset: their people.
To summarize the path forward:
- AI augments, it does not replace. It automates tasks, freeing human talent to focus on the strategic, creative, and complex work that drives real value.
- Human skills are becoming more valuable, not less. In a world of infinite data and automated analysis, the ability to think critically, create, and connect with others is the new competitive premium.
- Operational efficiency is the gateway to strategic capacity. By using AI to streamline your operations, you are not just cutting costs; you are buying back time and cognitive bandwidth for your team to innovate and win.
Ultimately, AI will affect your operations and people by creating a new, synergistic partnership between human intelligence and machine capability. It will demand new skills, new workflows, and new ways of thinking about value creation. The journey begins not with a massive technology investment, but with a simple, strategic question.
Look at your team, your processes, and your biggest challenges, and ask yourself: "What is the single most repetitive, low-value task my team performs, and what could they truly achieve if AI gave them all that time back?"
The answer to that question is the starting point for your AI-powered future. If you're ready to explore how a tailored, custom-built AI solution can help you answer it, let's talk.
About Baytech
At Baytech Consulting, we specialize in guiding businesses through this process, helping you build scalable, efficient, and high-performing software that evolves with your needs. Our MVP first approach helps our clients minimize upfront costs and maximize ROI. Ready to take the next step in your software development journey? Contact us today to learn how we can help you achieve your goals with a phased development approach.
About the Author

Bryan Reynolds is an accomplished technology executive with more than 25 years of experience leading innovation in the software industry. As the CEO and founder of Baytech Consulting, he has built a reputation for delivering custom software solutions that help businesses streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth.
Bryan’s expertise spans custom software development, cloud infrastructure, artificial intelligence, and strategic business consulting, making him a trusted advisor and thought leader across a wide range of industries.


